Pathology
Pathology is the study of disease. It is the bridge between science and medicine. It underpins every aspect of patient care , from diagnostic testing and treatment advice to using cutting- edge genetic technologies and preventing disease. Doctors and scientists working in pathology are experts in illness and diseases. They use their expertise to support every aspect of healthcare ,from guiding doctors on the right way to treat common diseases , to using cutting- edge genetic technologies to treat patients with life threatening conditions Pathology is a branch of medical science primarily concerning the cause, origin, and nature of disease. It involves the examination of tissues, organs, bodily fluids, and autopsies in order to study and diagnose disease.
Ultrasonography
Ultrasound imaging uses a transducer or probe to generate sound waves and produce pictures of the body's internal structures. It helps diagnose the causes of pain, swelling and infection in the body's internal organs and to examine an unborn child (fetus) in pregnant women. In infants, doctors commonly use ultrasound to evaluate the brain, hips, and spine. It may also be used to provide imaging guidance to needle biopsies or to see and evaluate conditions related to blood flow. Ultrasound is safe, noninvasive, and does not use radiation. This procedure requires little to no special preparation. Your doctor will tell you how to prepare, including whether you should not eat or drink beforehand. Leave jewelry at home and wear loose, comfortable clothing. You may need to change into a gown.
Echocardiography
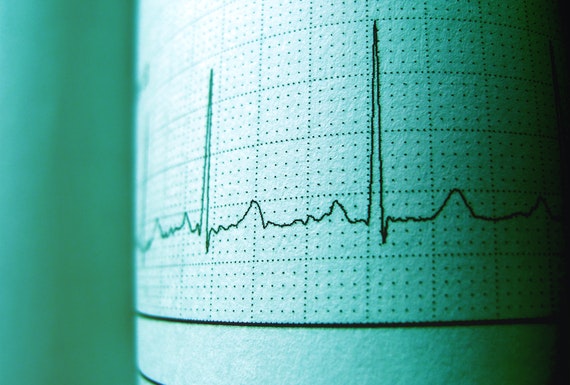
It refers to a test that measures the electrical activity of the heart to show whether or not it is working normally. An ECG records the heart’s rhythm and activity on a moving strip of paper or a line on a screen. The ECG is one of the most commonly used medical studies in the assessment of cardiovascular disease. It is the most important test for interpretation of the cardiac rhythm, detection of myocardial ischemia and infarction, conduction system abnormalities, pre-excitation, long QT syndromes, atrial abnormalities, ventricular hypertrophy, pericarditis, and other conditions.
Electrocardiogram (ECG) records the electrical impulses when the heart is beating. These impulses are recorded on a moving strip of paper or on a screen, i.e. it shows heart’s electrical activity as line tracings on paper. The spikes and dips that appear in the tracings are called waves. There are three main components to an ECG: the P wave, which represents the depolarization of the atria; the QRS complex, which represents the depolarization of the ventricles; and the T wave, which represents the repolarization of the ventricles.
If you have a heart problem or have any kind of problem, this procedure is done, which is considered a risk-free process. This is done by placing electrodes at specific places on your body such as hands, feet or chest.
We need the ECG to explore these important things, which are considered important.
Wall thickness of the heart
Abnormal heart rhythm
Heart attack in the past
Cholesterol accumulation due to chest pain
Diabetic, hypertensive person
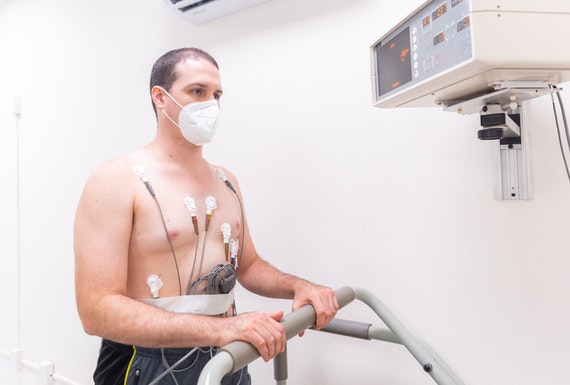
Holter monitor
A Holter monitor is a small, wearable electrocardiogram (ECG) device that keeps track of the heart rhythm during everyday activities. It's typically worn for a day or two. A health care provider uses the information captured on the device to help diagnose a heart rhythm problem (arrhythmia)
How the Test is Performed
Electrodes (small conducting patches) are stuck onto your chest. These are attached by wires to a small recording monitor. You carry the Holter monitor in a pocket or pouch worn around your neck or waist. The monitor runs on batteries.
Electrodes must be firmly attached to the chest so the machine gets an accurate recording of the heart's activity.
While wearing the device, avoid:
• Electric blankets
• High-voltage areas
• Magnets
• Metal detectors
Continue your normal activities while wearing the monitor. You may be asked to exercise while being monitored if your symptoms have occurred in the past while you were exercising.
X-Ray
X-rays are a type of radiation called electromagnetic waves. X-ray imaging creates pictures of the inside of your body. The images show the parts of your body in different shades of black and white. This is because different tissues absorb different amounts of radiation. Calcium in bones absorbs x-rays the most, so bones look white. Fat and other soft tissues absorb less and look gray. Air absorbs the least, so lungs look black. The most familiar use of x-rays is checking for fractures (broken bones), but x-rays are also used in other ways. For example, chest x-rays can spot pneumonia. Mammograms use x-rays to look for breast cancer.

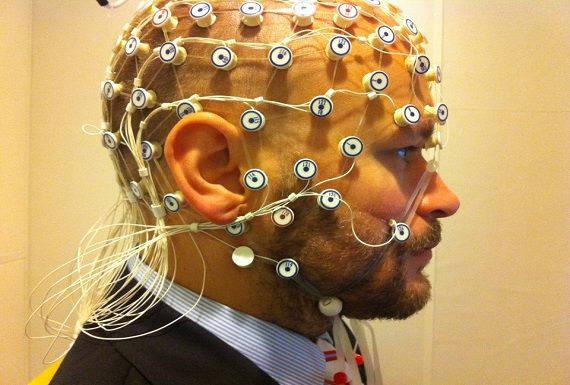
Electroencephalogram (EEG)
An electroencephalogram (EEG) is a test that detects electrical activity in your brain using small, metal discs (electrodes) attached to your scalp. Your brain cells communicate via electrical impulses and are active all the time, even when you're asleep. This activity shows up as wavy lines on an EEG recording.
An EEG is one of the main diagnostic tests for epilepsy. An EEG can also play a role in diagnosing other brain disorders. EEGs are safe and painless
An EEG can determine changes in brain activity that might be useful in diagnosing brain disorders, especially epilepsy or another seizure disorder. An EEG might also be helpful for diagnosing or treating the following disorders:
• Brain tumor
• Brain damage from head injury
• Brain dysfunction that can have a variety of causes (encephalopathy)
• Inflammation of the brain (encephalitis)
• Stroke
• Sleep disorders
NCV (Nerve Conduction Velocity)
A nerve conduction velocity test (NCV) is an electrical test that is used to determine the adequacy of the conduction of the nerve impulse as it courses down a nerve. This test is used to detect signs of nerve injury. In this test, the nerve is electrically stimulated, and the electrical impulse 'down stream' from the stimulus is measured. This is usually done with surface patch electrodes (they are similar to those used for an electrocardiogram) that are placed on the skin over the nerve at various locations. One electrode stimulates the nerve with a very mild electrical impulse. The resulting electrical activity is recorded by the other electrodes. The distance between electrodes and the time it takes for electrical impulses to travel between electrodes are used to calculate the speed of impulse transmission (nerve conduction velocity). A decreased speed of transmission indicates nerve disease or abnormal pressure on the nerve. A nerve conduction velocity test is often done at the same time as an electromyogram (EMG). An EMG is carried out in order to exclude or detect muscle conditions which may be present due to muscular or neurologic disease.